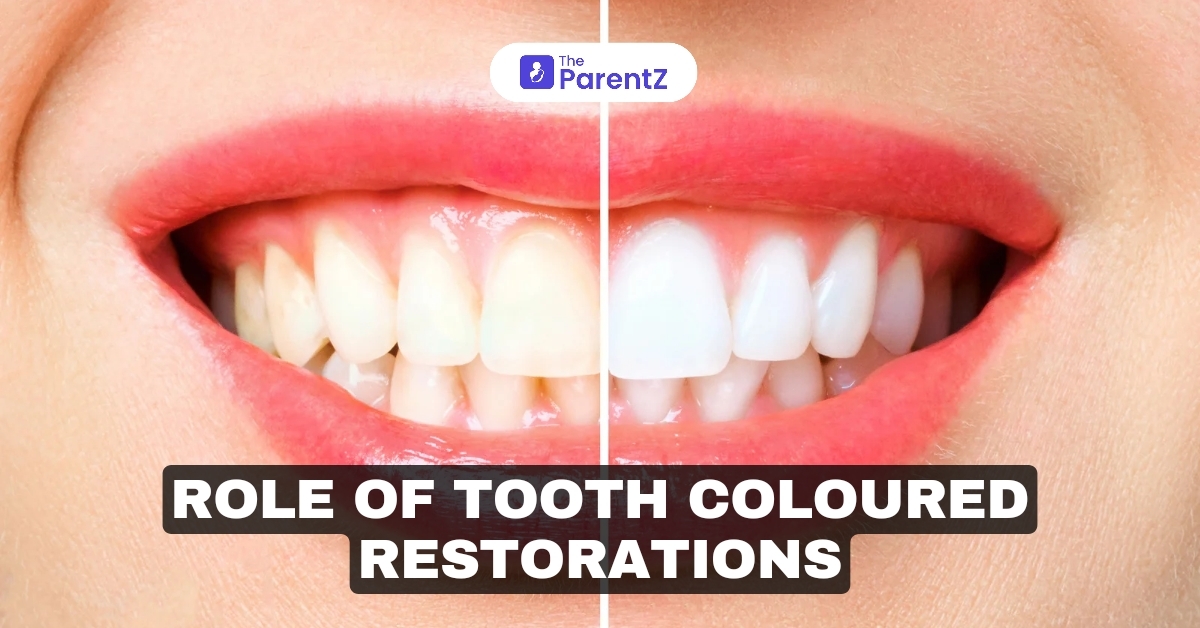
Tooth-colored restorations have revolutionized modern dentistry by offering patients natural-looking, durable solutions for damaged or decayed teeth. Unlike traditional materials, such as amalgam, tooth-colored restorations blend seamlessly with the natural tooth, providing both aesthetic and functional benefits. As dental technology advances, these restorations have become stronger and more versatile, making them a preferred choice for patients and clinicians alike. This article explores the role of tooth-colored restorations, their indications, contraindications, advancements, and why they are essential in contemporary dental practice.
Indications for Tooth-Colored Restorations
Tooth-colored restorations are commonly used in various clinical scenarios, including:
- Cavities: When decay needs to be removed and the tooth restored with a filling.
- Fractures or Chips: To repair chipped or fractured teeth while maintaining natural aesthetics.
- Worn Teeth: To restore teeth worn down by grinding (bruxism) or erosion.
- Cosmetic Enhancements: For improving the shape, size, or color of a tooth.
- Diastema Closure: To close gaps between teeth with a minimally invasive approach.
- Replacing Amalgam Fillings: Patients desiring to replace old silver fillings for a more natural appearance.
Contraindications for Tooth-Colored Restorations
While tooth-colored restorations are versatile, there are situations where they may not be suitable:
- Large Areas of Damage: In cases of extensive tooth damage, stronger materials like crowns or onlays may be more appropriate.
- Heavy Bite Forces: Patients with habits like bruxism may not be ideal candidates for composite restorations due to the increased wear and risk of fractures.
- Deep Cavities: In instances where the cavity extends too close to the pulp, other restorative techniques like indirect restorations may be preferred.
Advancements in Tooth-Colored Restorations
The field of restorative dentistry has seen significant advancements in the materials and techniques used for tooth-colored restorations:
- Nanocomposite Resins: These materials offer enhanced strength, polishability, and longevity, making them more resistant to wear and discoloration.
- Improved Bonding Agents: Modern bonding techniques ensure a stronger, more reliable bond between the restoration and the tooth, reducing the likelihood of leakage or detachment.
- CAD/CAM Technology: Computer-aided design and manufacturing allow for precise and custom-made restorations, enhancing the fit and reducing chair time for patients.
- 3D Printing: This technology has paved the way for faster production of indirect tooth-colored restorations, such as inlays and onlays, providing high precision and aesthetic appeal.
Use of Tooth-Colored Restorations
Tooth-colored restorations are used in both direct and indirect restorative procedures:
- Direct Restorations: Typically, composites are used to fill cavities or repair minor fractures directly in the patient’s mouth. This technique is often completed in one visit.
- Indirect Restorations: For more extensive repairs, such as inlays, onlays, or veneers, tooth-colored materials are fabricated outside of the mouth and bonded onto the tooth in a second appointment. Materials used in indirect restorations include ceramic and composite resins.
Benefits of Tooth-Colored Restorations Over Other Materials
Tooth-colored restorations offer several advantages over traditional materials like amalgam or gold:
- Aesthetics: The most significant advantage is their ability to mimic the natural appearance of teeth, making them virtually indistinguishable from the surrounding dentition.
- Conservation of Tooth Structure: Tooth-colored materials bond to the tooth, allowing for more conservative preparations compared to amalgam, which requires removal of healthy tooth structure for mechanical retention.
- Bio compatibility: Modern composite materials are mercury-free, offering a safer option for patients concerned about the potential health risks associated with amalgam fillings.
- Durability: With advancements in materials, tooth-colored restorations have become more durable and wear-resistant, offering long-term results for patients.
- Minimal Sensitivity: Patients often experience less post-operative sensitivity compared to metal restorations, which conduct temperature more easily.
Why Tooth-Colored Restorations Are Important
Tooth-colored restorations play a crucial role in modern dental care due to their blend of aesthetics, functionality, and patient comfort. These restorations allow dentists to maintain the structural integrity of the tooth while offering patients a visually appealing result. As dental materials and techniques continue to evolve, the importance of tooth-colored restorations will only increase, providing patients with durable, natural-looking options for maintaining their oral health.
Conclusion
The role of tooth-colored restorations in dentistry cannot be overstated. With the ability to provide both aesthetic and functional benefits, they have become the standard of care for many restorative procedures. As advancements in dental materials and techniques continue, the options for patients will expand, offering even more durable and lifelike solutions. By understanding the indications, contraindications, and benefits of tooth-colored restorations, both patients and clinicians can make informed decisions to achieve optimal oral health and satisfaction.




Be the first one to comment on this story.